Machine Learning
Explainable AI for Deepfake Detection

The objective of this project was to incorporate explainable AI (XAI) techniques to gain insights into the interpretability of the model. The project utilizes state-of-the-art XceptionNet architecture to detect deepfakes, and then employs LIME and GradCam algorithms to visualize and analyze how the model interprets the results.
We extracted frames from FaceForensics ++ and CelebDF video dataset and trained the Xceptionet model pretrained on ImageNet weights and were able to achieve an accuracy of 0.99.
Terrain Identification from Time Series Data
This is a classification task to find different terrains from time series data. The idea is to train a neural network using given data to classify which terrain an unknown data represents. Class label 0 represents “standing/walking” 1 represents “going downstairs” 2 : “going upstairs” And 3: “walking on grass”. We use F1 macro score as the evaluation metric.
The repository contains 3 Jupyter notebooks: NN_C1.ipynb, NN_C2.ipynb and NN_C3.ipynb.
- NN_C1 runs a random forest model for predictions
- NN_C2 uses 2 1D CNN model
- NN_C3 uses a BiLSTM model.
ECE 792 Advanced Machine Learning Coursework
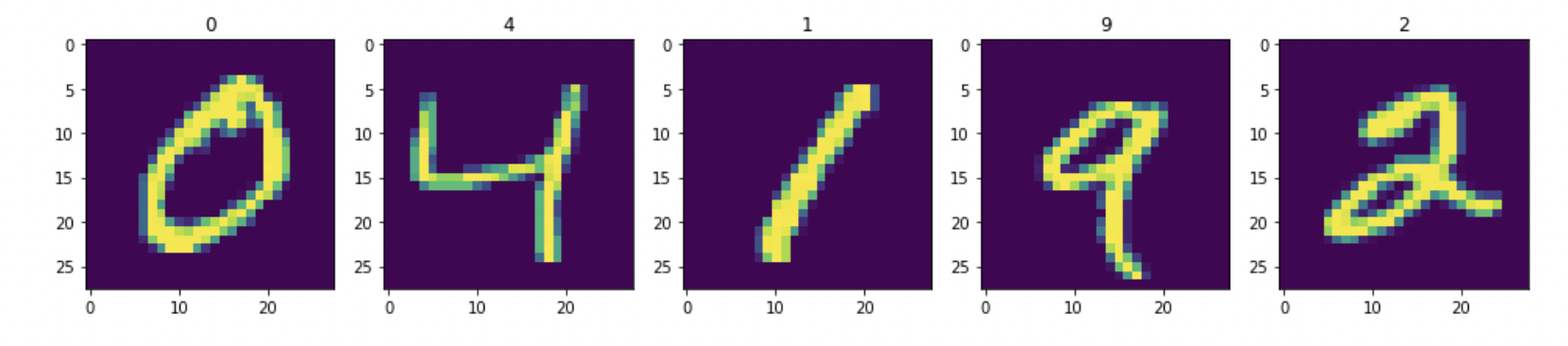
- Implemented CNN on MNIST dataset and Performed Deconvolution: Convolution, Deconvolution, CNN, Multilayer Perceptron, Batchnorm, Layernorm, Dropout, Maxpool.
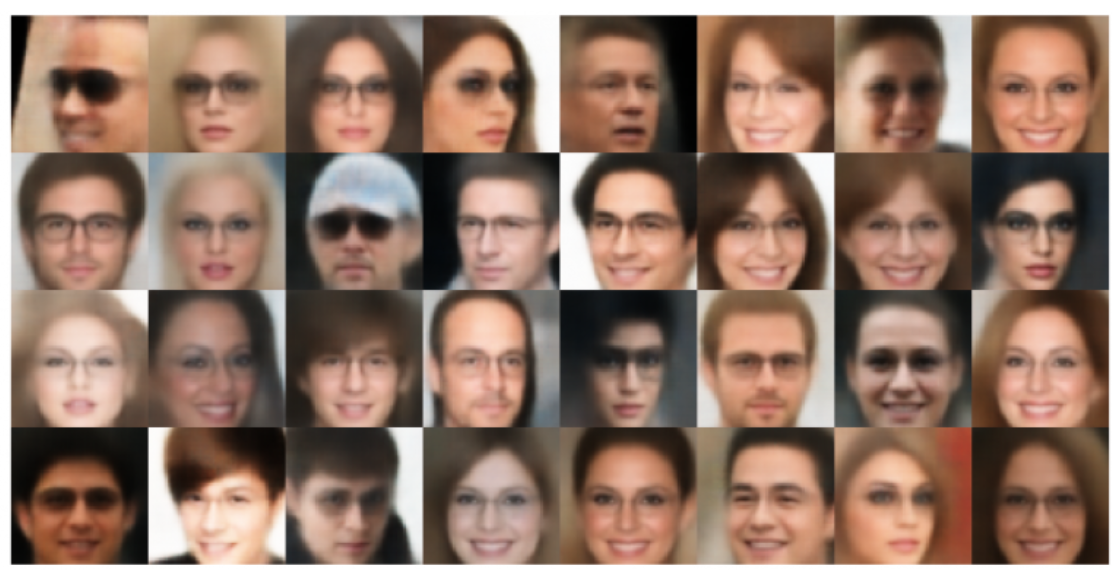

-
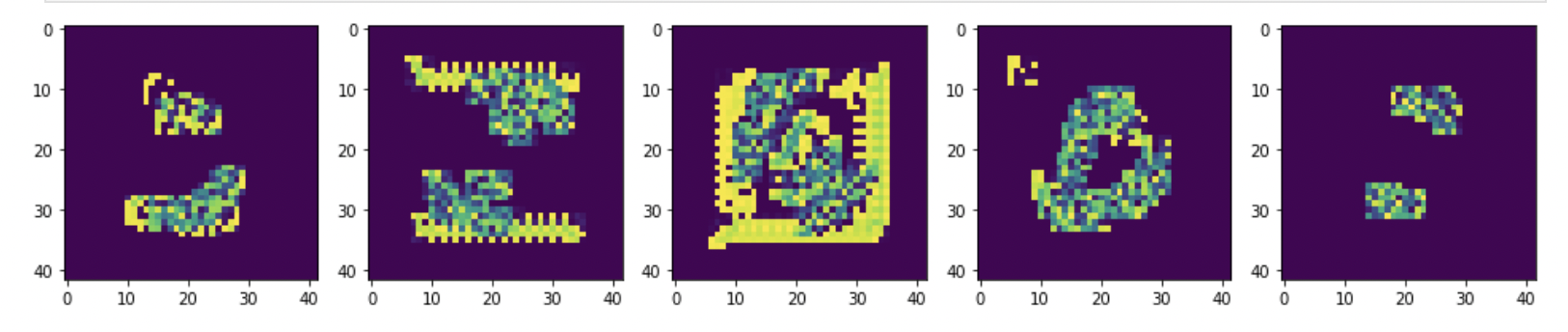
Implemented Conditional Variational Autoencoder on CelebA dataset
- Developed and trained a CVAE to encode and manipulate images in CelebA database.
- Used the previusly trained CVAE to manipulate an image by changing the attribute vector input to the encoded image.

-
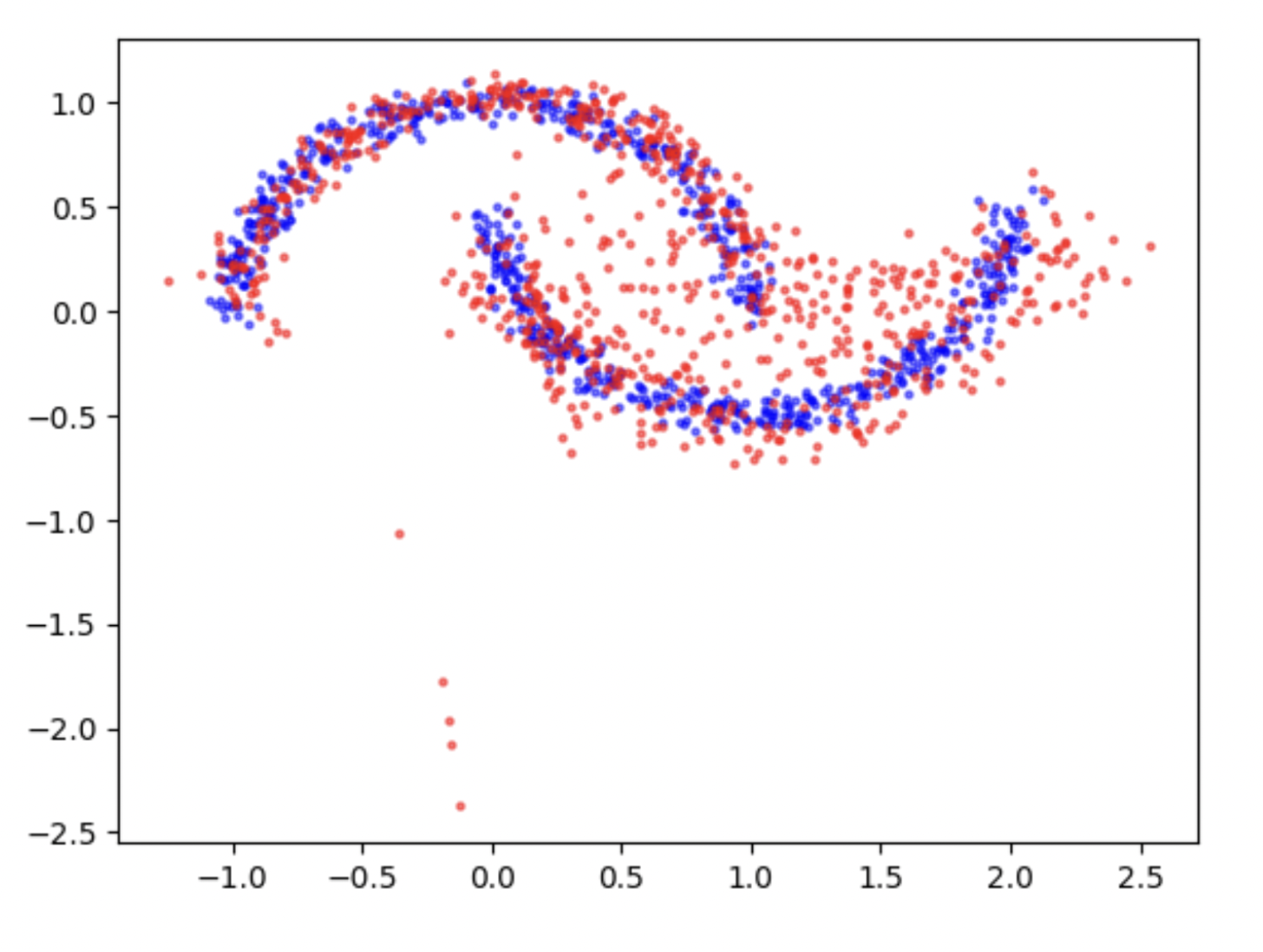
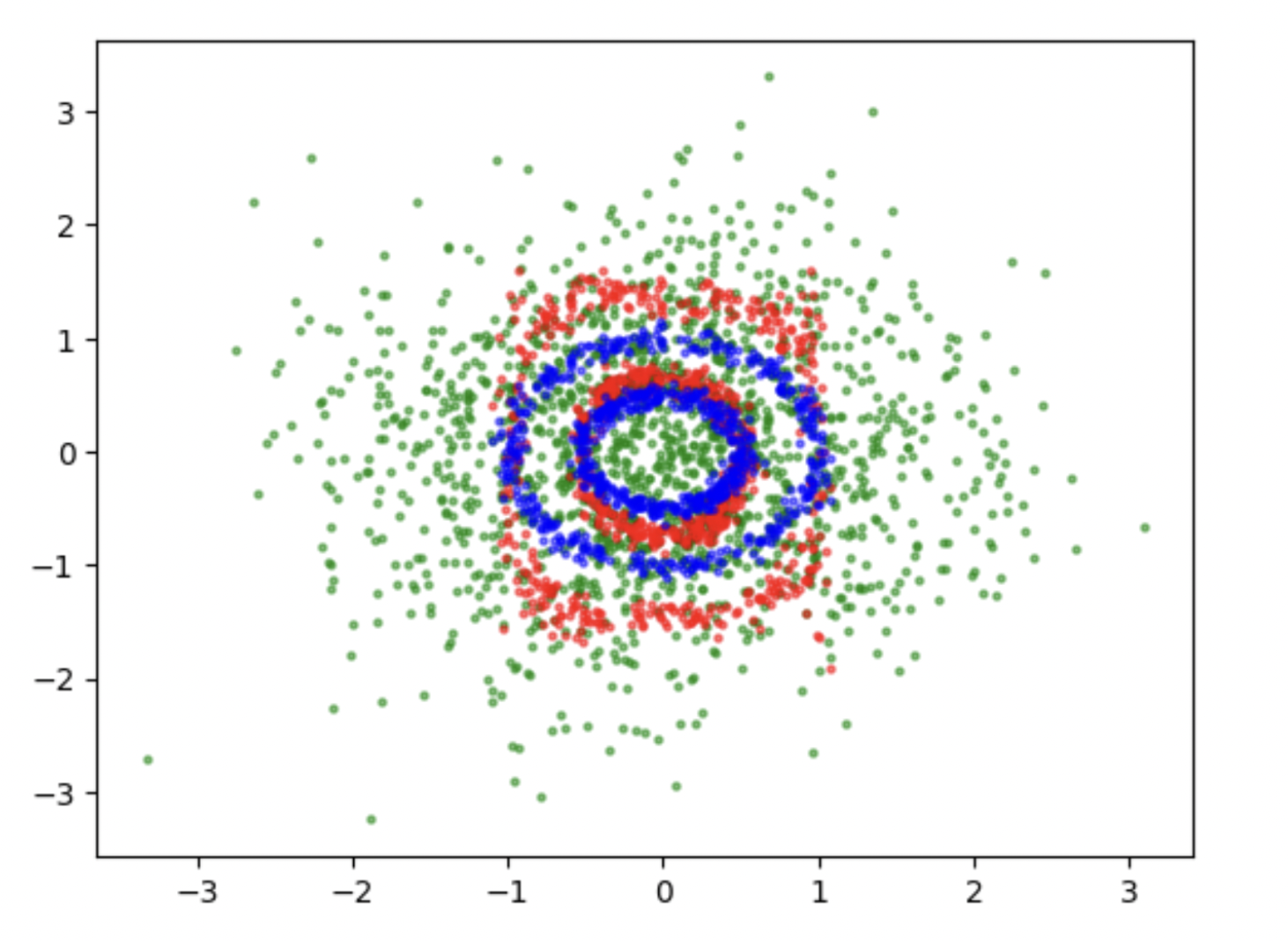
Implemented Normalizing Flows architecture
The project involves designing a Normalizing Flow architecture with two transformations, f : x 7→ z and f−1 : z 7→ x where f takes a point, x belonging to the same distribution as one of the datasets, as input, and tries to transform it into z ∼ N(0,I2), where 0 = [0,0]T, and I2 is the 2×2 identity matrix. f−1 would be the inverse of f.
-
Implemented LSTM model to predict the next word of a sentence
Generated a 6 gram dataset and used categorical cross-entropy along with Adam optimizer to train the model.
-
Trained a Graphical Convolutional Network (GCN) to classify nodes in Zachary’s Karate Club dataset
Computer Vision
Laplacian Blob Detector
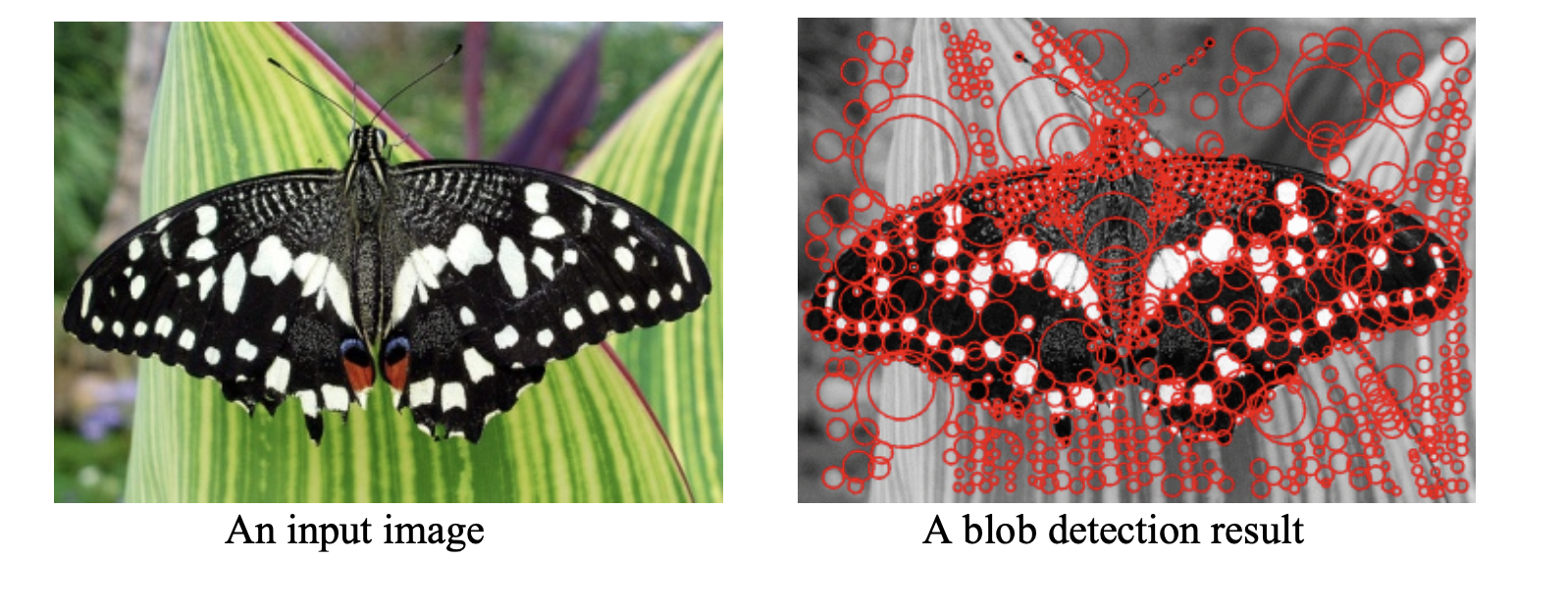

The idea of a Laplacian blob detector is to convolve the image with a “blob filter” at multiple scales and look for extrema of filter response in the resulting scale space.
Blob Filter:
This filter generated by double derivating Gaussian filter along x and y-axis and adding them. Above is also known as Laplacian of Gaussian. The Laplace is the sum of second derivatives (the trace of the Hessian matrix). An image convolved with the LoG is the same as the Laplacian of an image convolved with a Gaussian:
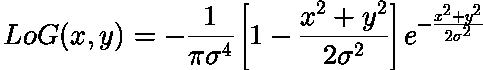
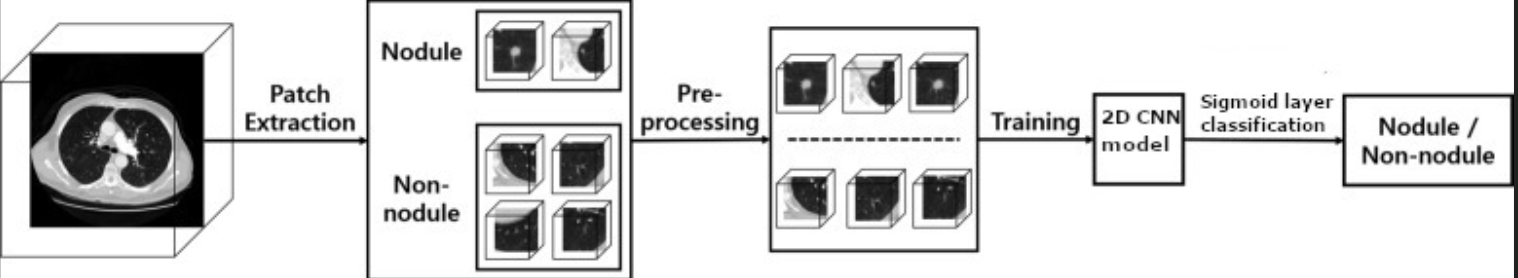
Comparative Analysis of 3D & 2D CNN for Lung Cancer Nodule Detection
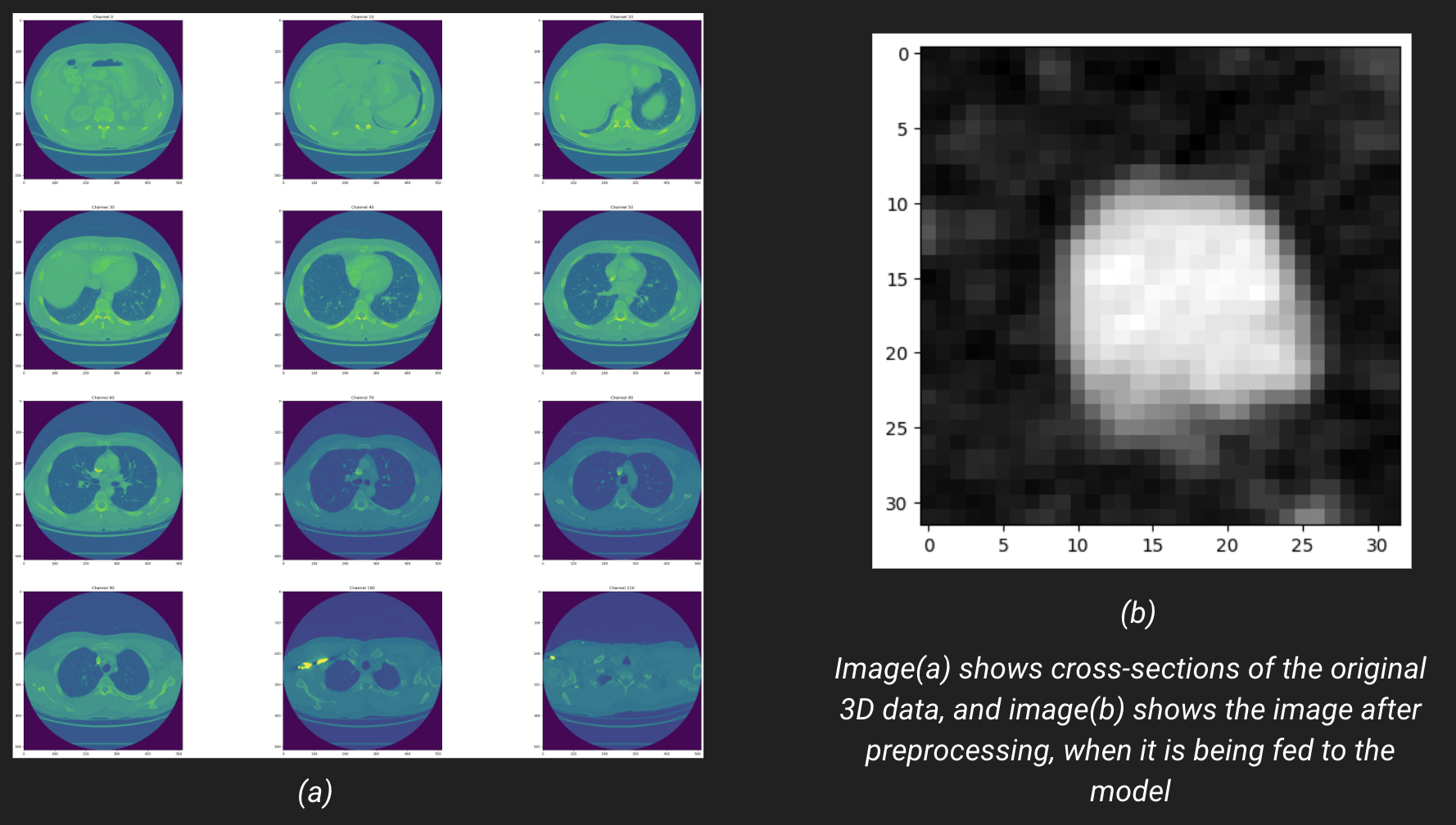
Created 2D and 3D CNN VGG-16 models to detect lung cancer with 79% and 91% sensitivity using Luna16 DICOM images.
Conducted data preprocessing for nodule patch extraction, performed voxel coordinate conversion. Applied data augmentation techniques to enhance the dataset’s diversity and model robustness
Implemented 2D FFT in Python from scratch
-
a. Wrote a function to implement g= conv2(f, w, pad), where f is an input image (grey, or RGB), w is a 2-D kernel (e.g., 3 × 3 box filter), and pad represents the 4-padding type clip/zero-padding, wrap around, copy edge, and reflect across edge.
b. Created a grey image of size 1024x1024 pixels that consists of a unit impulse at the center of the image (512, 512) and zeros elsewhere. Used this image and a kernel (e.g., selected one from (a)) to confirm that the function is indeed performing convolution.
-
Implementing and testing the 2-D FFT and its inverse using a built-in 1-D FFT algorithm.
Natural Language Processing
Modeling Food Web and Forecasting Populations for Endangered Wildlife Species
Collaborated with Endangered Wildlife OU ̈ through Omdena to build an automated data collection & extraction tool.
-
Leveraged Beautiful Soup, Google Search API and journal parsing libraries such as pytesseract, sciparse and tabula for efficient data extraction from PDFs and web sources.
- Developed a Haystack BERT Question- Answering model to track the population of various species over time.
- Integrated with Streamlit and AWS RDS to give the results in a csv file and upload to the database.
LOLgorithm : Integrating Semantic, Syntactic, and Contextual Elements for Humor Classification
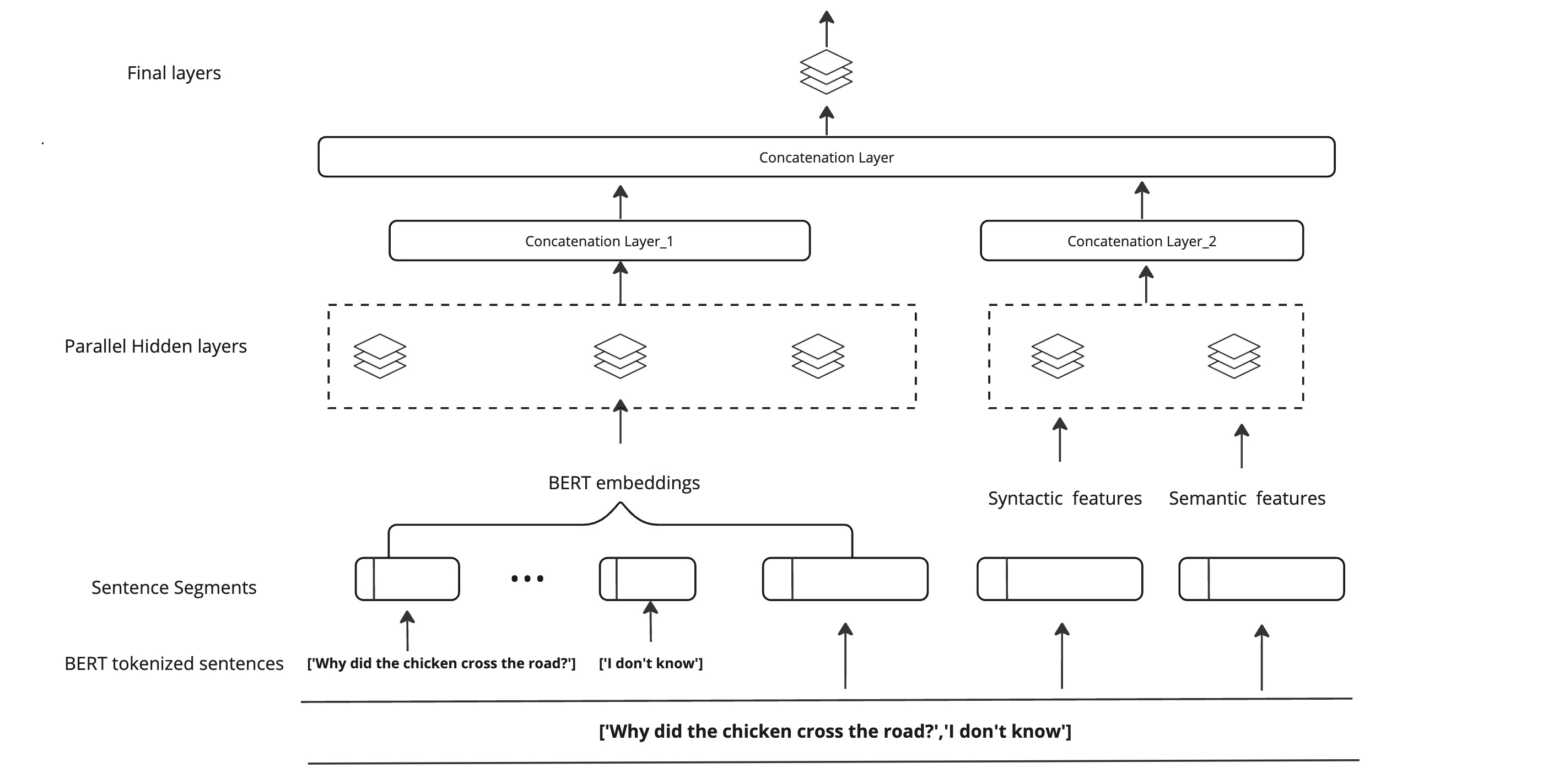
-
Formulated humor recognition as a classification task distinguishing between humorous and non-humorous instances.
-
Explored the syntactical structure involves leveraging Lexicons to capture sentiment counts within a sentence, while Statistics of Structural Elements (SSE) encapsulates the statistical insights of Noun phrases, Word phrases, and more.
-
Unveiled the semantic layers of humor delves into Word2Vec embeddings, analyzing incongruity, ambiguity, and phonetic structures within sentences. Additionally, contextual information was harnessed through ColBERT embeddings. For each latent structure, a set of features were designed to capture the potential indicators of humor.
Increased the F1 score for the SOTA Colbert model from 50% to 62%, showcasing a 24% improvement in performance on unseen data.
Prompt Engineering for Question Answering
-
Conducted in-depth exploration of Large Language Model (LLM) capabilities with a focus on prompt engineering for question answering applications.
-
Experimented with various prompt strategies such as few-shot, chain-of-thought, Generated Knowledge and other parameters to assess their impact on question answering performance using the SQUAD2.0 dataset
-
Evaluated performance metrics such as F1 score, Exact Match (EM) score, Bi-Encoder Score, Semantic Answer Similarity (SAS) metric, Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU), and ROUGE Score for a thorough analysis of the task outcomes.
Event Classification through Word Embedding Exploration
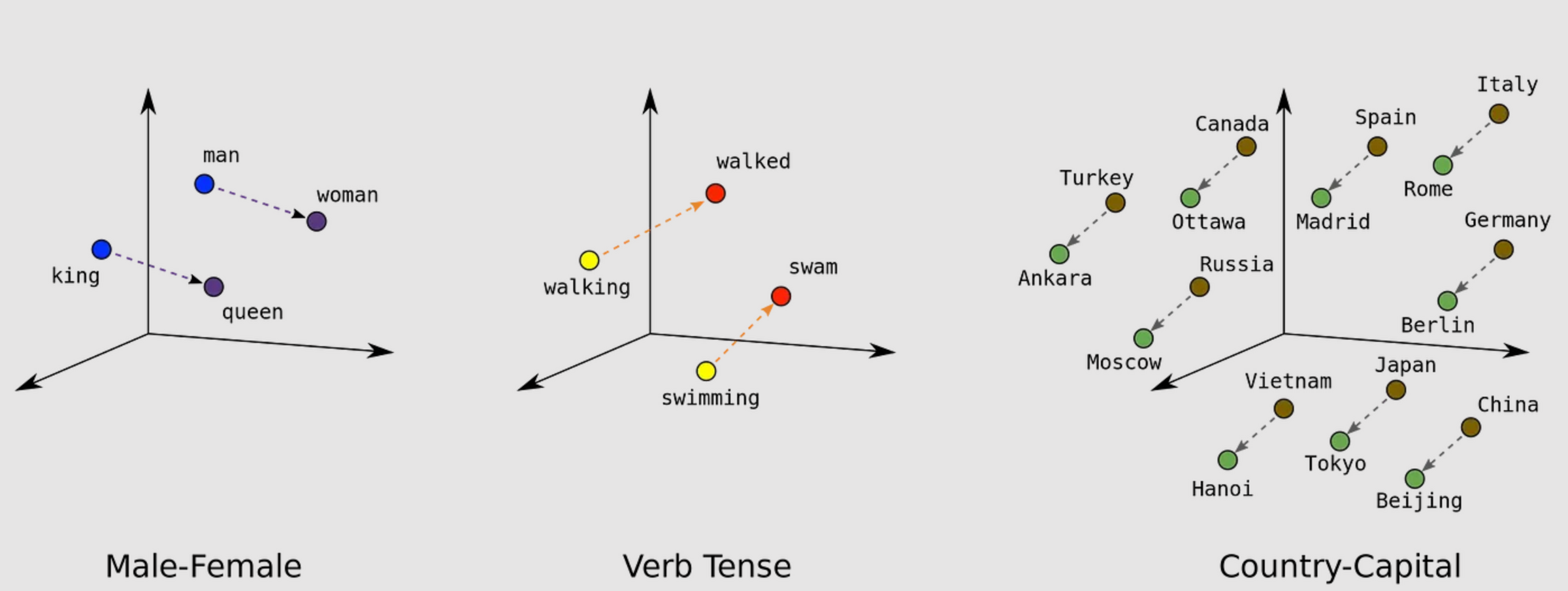
- Implemented effective embedding schemes such as TF-IDF, Sentence Bert Embedding, InferSent, Doc2Vec and GloVe on a news snippet dataset.
- Employed nearest neighbor search using cosine similarity for classification and evaluated the top-k accuracy for different embeddings.
- Surpassed TF-IDF baseline with substantial performance improvement.
Signal Processing
Kalman Filter Implementation in Matlab
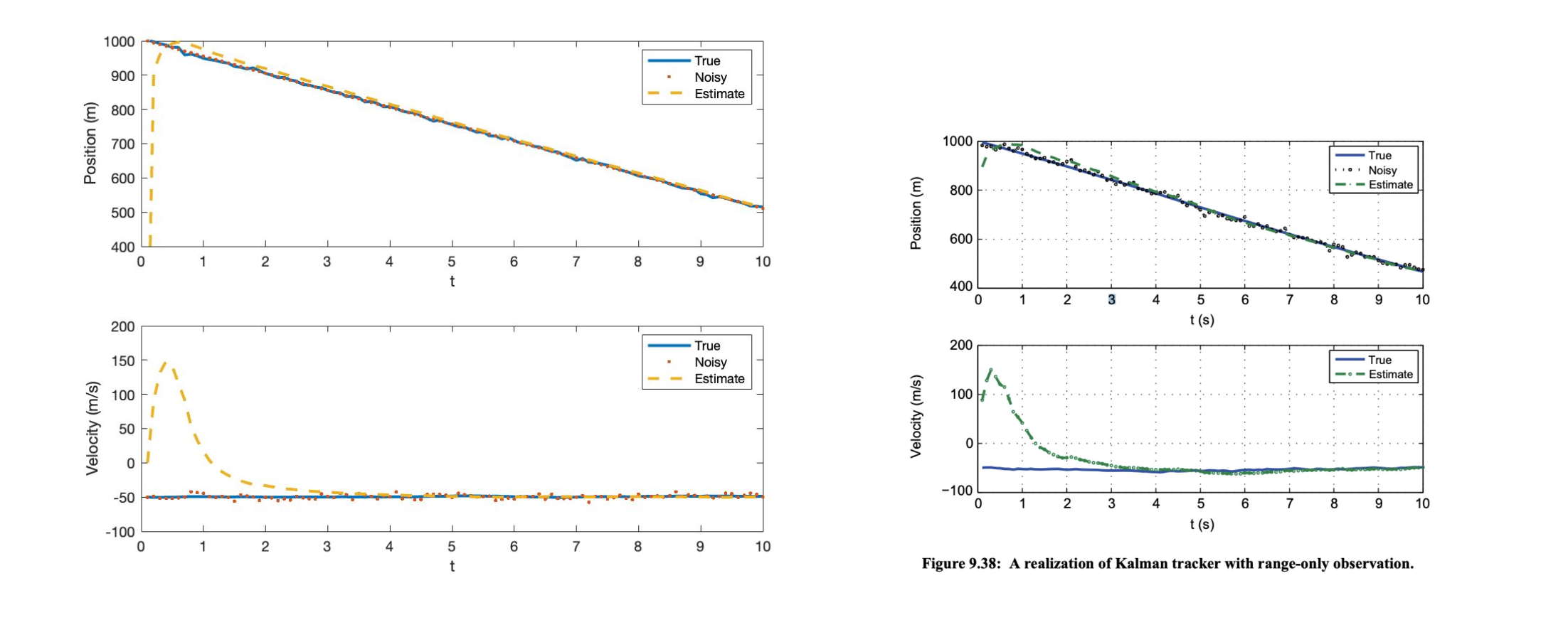
Kalman filter estimates the state of a system with incomplete or noisy information.
- It uses the system model and the measurements to estimate the true state of the system and its uncertainty.
- In this project, I implemented a discrete-time, time-invariant Kalman filter as a MATLAB function.
- For the benchmark case I used the Kalman filter to estimate the position and velocity of a moving object based on noisy measurements of its position.
- Kalman filter will be used to make future predictions using past values to correct the estimated state.
Convergence and Simulation of Random Variables using Matlab
This project involves simulation, transformation and convergence of Random Variables using concepts underlined in: “Understanding Convergence Concepts: A Visual-Minded and Graphical Simulation- Based Approach’
FFT Implementation in MATLAB
For this assignment, I implemented three functions in MATLAB®:
- myDFT, a brute-force implementation of the DFT,
- myFFT_139, a decimation-in-time implementation of the FFT, and
- “butterfly”, a decimation-in-time butterfly called by myFFT_139. A code listing for these functions is provided in the appendix.
Simulations in MATLAB
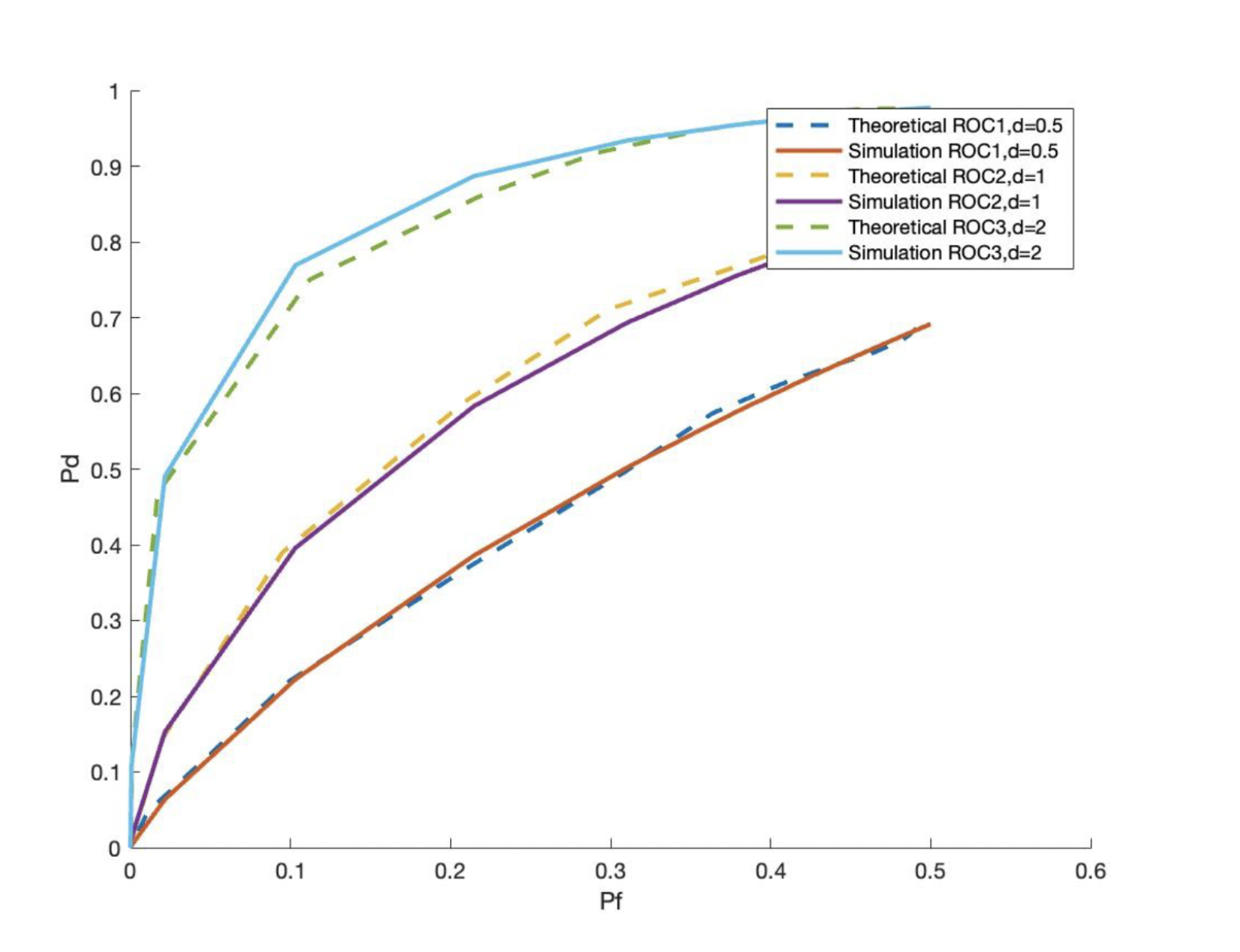
- Monte Carlo Simulation
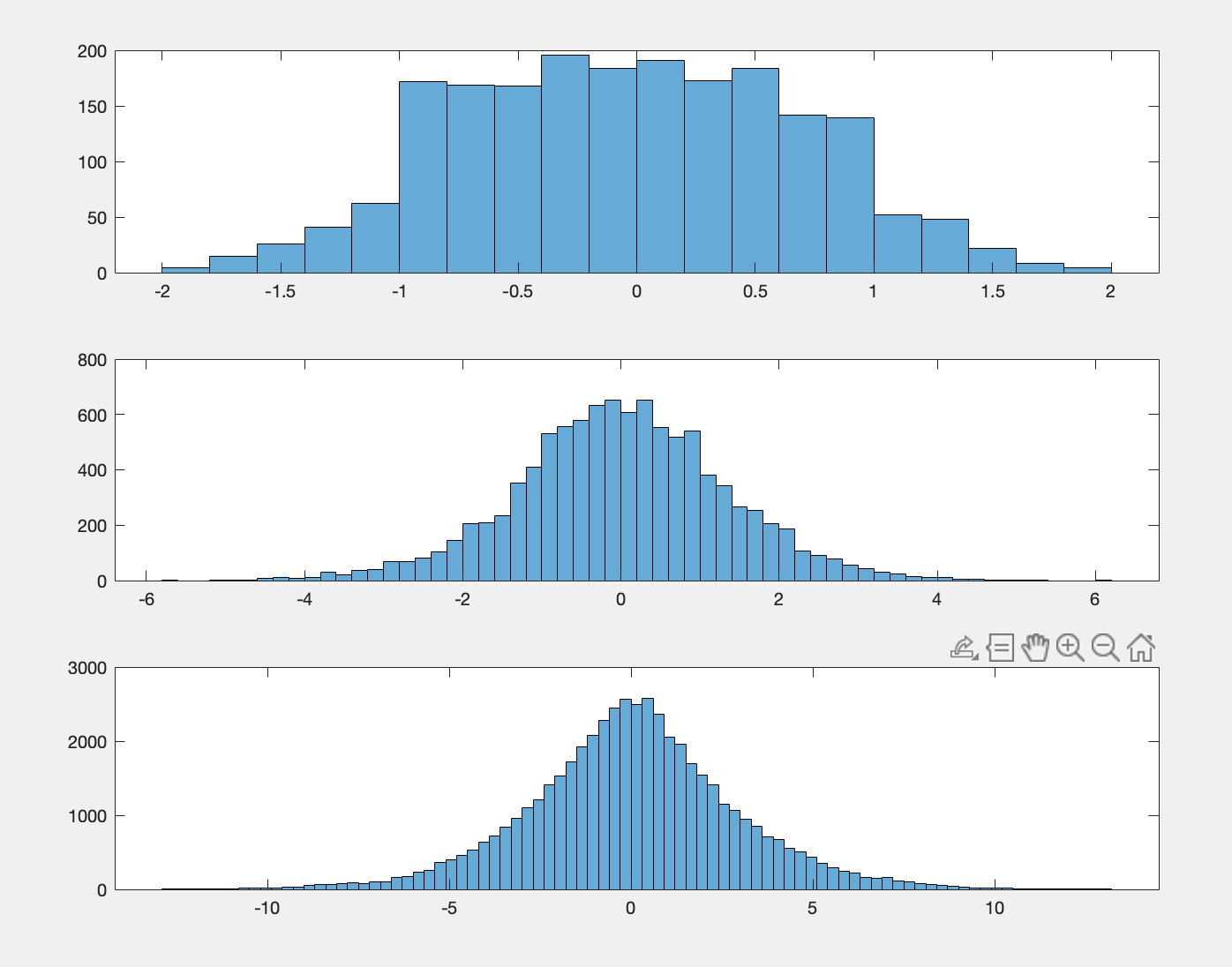
- Implementation of Central Limit theorem
Cloud Computing
Health Monitoring Wearables and Cloud Integration
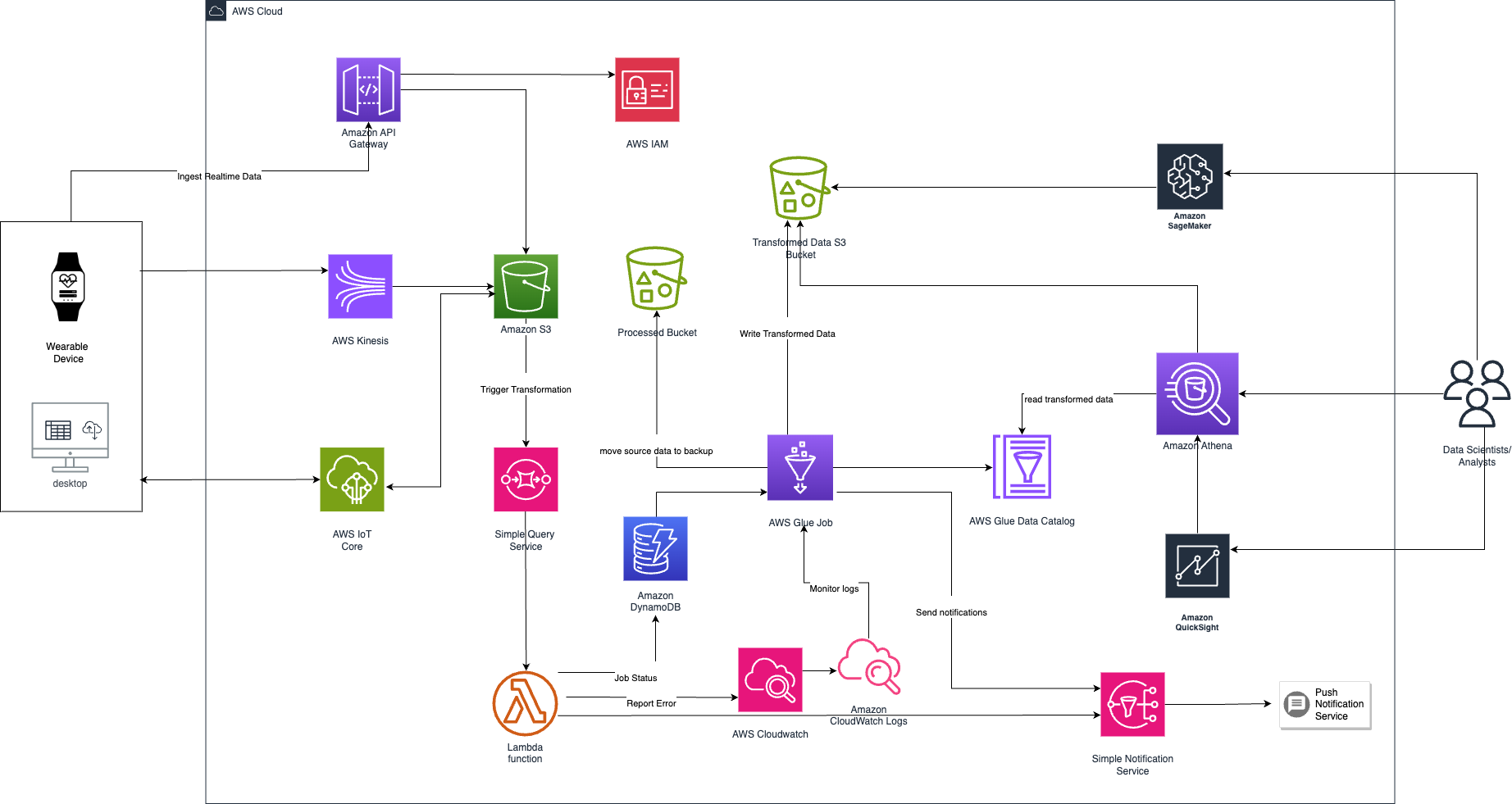
This project aims to create a seamless ecosystem where wearable health devices and cloud computing converge to redefine healthcare. It establishes a secure, scalable, and interoperable cloud-based infrastructure for data collection, analysis, and secure sharing, while prioritizing security and privacy.
- Utilized Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) functionality for Dynamic Scaling.
- Generated the load using Minikube and analyzed the results using Locust monitoring.


